Queues aren’t always that simple. Depending on the need, the different Types of Queue in Data Structure that solve different kinds of problems efficiently.
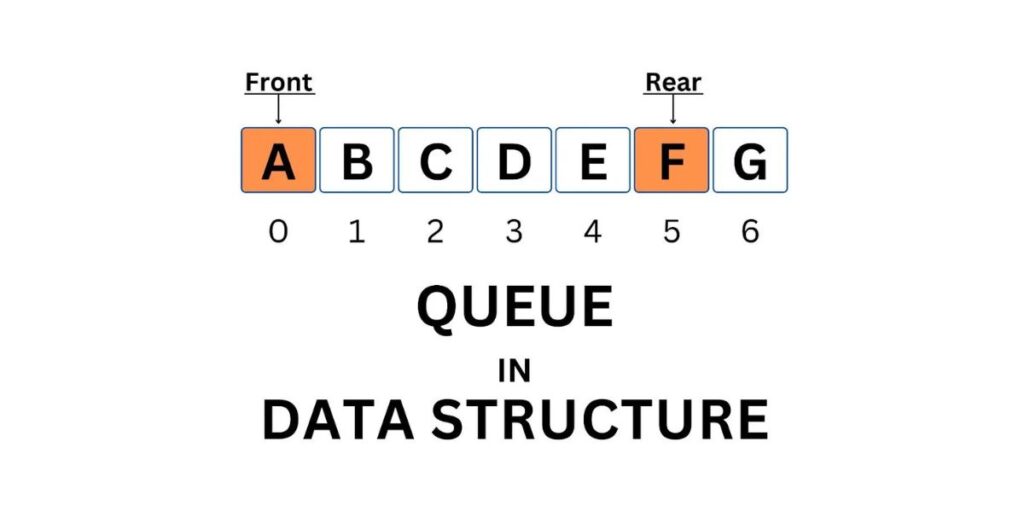
A queue is a linear structure in data structure which follows the FIFO (First In, First Out) principle. For example people are standing in a line in the hostel’s food stall where the first person will be served first so that person will be out first.
In this blog post, we will explore the types of queues in data structures, how they work, and where they are used.
Types of Queue in Data Structure
There are four types of Queue in Data Structure:
- Simple Queue
- Circular Queue
- Priority Queue
- Double-Ended Queue (Deque)
Do you want to learn about Stack and Queue…. Let’s Learn…
1. Simple Queue (Linear Queue)
A simple queue, also known as a linear queue, follows the basic FIFO principle. You insert (enqueue) items at the rear and remove (dequeue) them from the front.
Example:
- A line of people waiting in the queue for the food to be served in the hostel
- Print jobs lined up for a single printer.
Limitation:
- If the rear reaches the end, no more elements can be added even if the front has free space.
2. Circular Queue
A circular queue fixes the limitation of the simple queue by connecting the last position back to the first, forming a circle. This way, when the rear reaches the end, it moves to the front if space is available.
Example:
- CPU scheduling.
- Streaming buffers.
- Memory management.
Benefit:
- Utilizes space efficiently by reusing empty slots.
3. Priority Queue
A priority queue processes elements based on their importance, not just the order they arrived. Items with higher priority are processed first. If two items have the same priority, it uses FIFO among them.
Example:
- Emergency rooms (critical patients treated first).
- Task scheduling in computers (urgent tasks get CPU time first).
Types of Priority Queue:
There are two main types:
Ascending order (or min-priority queue) and Descending order (or max-priority queue)
4. Double-Ended Queue (Deque)
A Deque (Double-Ended Queue) allows insertion and deletion from both the front and rear. It’s a flexible structure that can work as both a queue and a stack.
Types of Deque:
There are two types of deques. These two types are due to the restrictions put to perform either the insertions or deletions only at one end. They are:
- Input-restricted deque
- Output-restricted deque
Quick Comparison Table
| Queue Type | Insertion | Deletion | Special Feature |
| Simple Queue | Rear | Front | Basic FIFO |
| Circular Queue | Rear (wraps around) | Front (wraps around) | Reuses empty space efficiently |
| Priority Queue | Rear (by priority) | Front (highest) | Served by priority |
| Deque | Front & Rear | Front & Rear | Insert/Delete from both ends |
Conclusion:
Queues are one of the most important data structures in computer science. Understanding the different types of queue in data structure — Simple Queue, Circular Queue, Priority Queue, and Deque — helps developers choose the right solution for various tasks like task scheduling, memory management, and customer service systems.
Each type has its own strengths depending on whether you need to process tasks in order, by priority, or with more flexibility.
FAQS:
What are the 4 types of queues?
Circular queue in data structure
What is circular queue and linear queue?
What is the difference between circular queue and circular linked list?
Priority queue in data structure
Types of priority queue in data structure
What is ascending and descending priority queue?
Types of deque in data structure
What are deques used for?