Think of how folders are organized on your computer — one main folder with many inside it. That’s exactly how a Tree Data Structure works. It starts from a single point (called the root) and branches out. Trees are used in file systems, search engines, and even in coding interviews. Once you understand the basics, they’re actually pretty easy to work with.
What is a Tree in Data Structures?
A Tree is a special type of data structure that looks like a real tree — with a root at the top and branches (nodes) below.
It is used to represent hierarchical data such as:
- Folder structures in a computer
- Family trees
- Organization charts
- XML/HTML document structure
- Binary search trees for fast searching
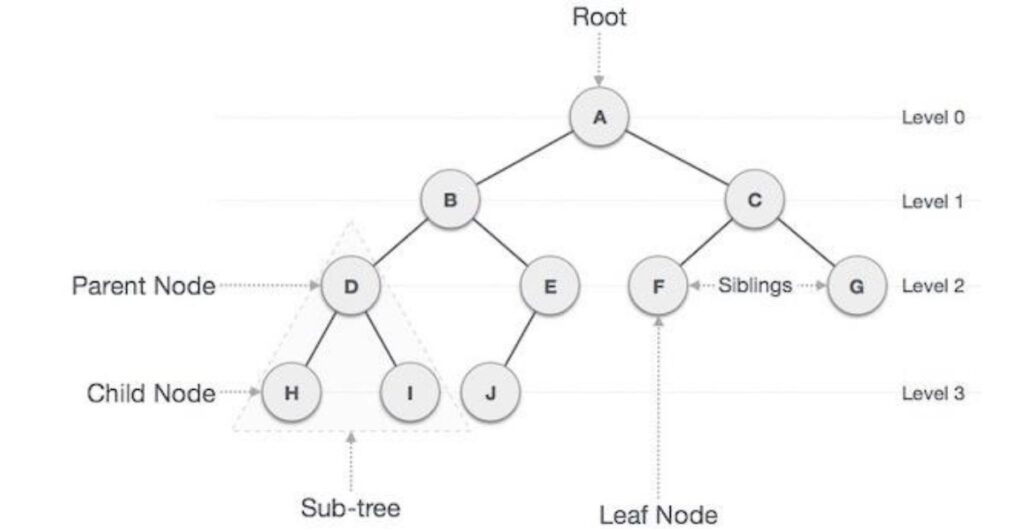
Basic Terminology
Term Meaning
Node – A single element in the tree
Root – The top-most node
Child – Node that comes from another node
Parent – Node that has one or more children
Leaf – A node with no children
Edge – The link between parent and child
Subtree – A small part of the tree that is also a tree
Height – Longest path from root to a leaf
Types of Trees
1. Binary Tree
A binary tree is a hierarchical data structure where each node has at most two children, typically referred to as the left child and the right child
2. Binary Search Tree (BST)
A binary search tree (BST) is a binary tree where every node in the left subtree is less than the root, and every node in the right subtree is of a value greater than the root
3. N-ary Tree
An n-ary tree is a hierarchical data structure where each node can have up to n children.
4. AVL Tree
An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree where the difference in height between the left and right subtrees of any node is at most one
5. Heap Tree
A heap is a specialized tree-based data structure that satisfies the heap property. This property ensures that for a min-heap, each node’s value is less than or equal to its children’s values, and for a max-heap, each node’s value is greater than or equal to its children’s values.
Tree Example (Visual)
A
/ \
B C
/ \ \
D E F
Root: A
B, C: Children of A
D, E: Children of B
Leaf Nodes: D, E, F
Tree in Python (Basic Node Class)
class Node:
def _init_(self, value):
self.value = value
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Example: Binary Tree
root = Node(“A”)
root.left = Node(“B”)
root.right = Node(“C”)
root.left.left = Node(“D”)
root.left.right = Node(“E”)
Where Trees Are Used?
Use Case Explanation
File System – Folder and file hierarchy
Web Pages (DOM Tree) – HTML is a tree structure
AI / Games – Decision trees for making choices
Databases – Indexing using B-trees, Trie, etc.
Compilers – Parse trees to understand code
Why to Learn Trees?
- Most common topic in coding interviews
- Used in real-life systems (file managers, databases, etc.)
- Teaches recursion, pointers, and optimization
More to Explore
Coming soon:
- Binary Search Tree implementation in Python
- Tree traversal techniques (Inorder, Preorder, Postorder)
- Interview questions on Trees
Final Words
Trees may look complex at first, but they’re everywhere in tech. Learning them will boost your coding, help with interview prep, and make you a better developer.
FAQS:
Tree data structure in python.
Types of Trees in Data Structures
What is tree in data structure?
Binary tree data structure.
Types of binary tree in data structure.
Binary search tree in data structure.
Avl tree in data structure.
N-ary tree in data structures.
Heap tree in data structures.
