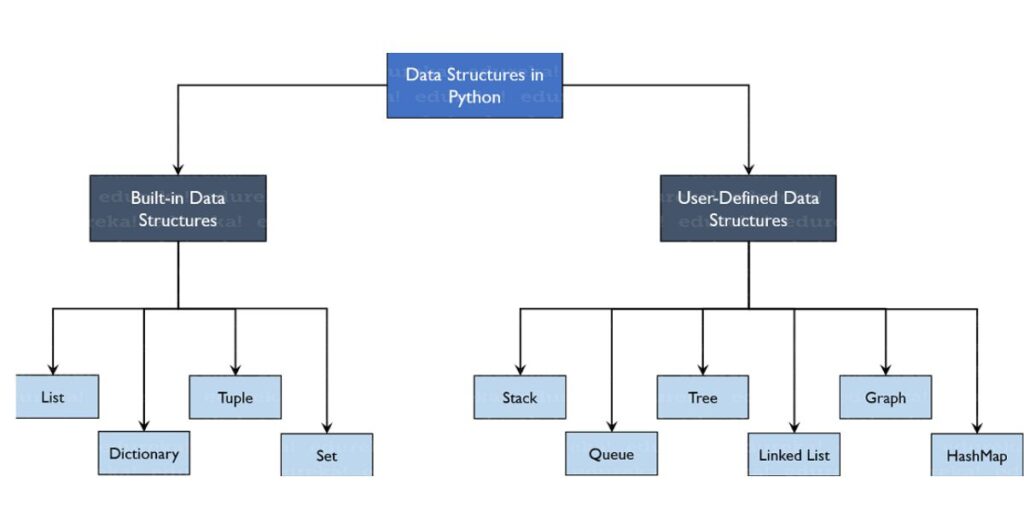
The basic Python Data Structures in Python include list, set, tuples, and dictionary. Each of the data structures is unique in its own way. Data structures are “containers” that organize and group data according to type.
What Are Data Structures?
A Data Structure is a collection of data values, the relationships among them, and the functions or operations that can be applied to the data, i.e., it is an algebraic structure about data.
In Python, data structures help you:
- Store multiple values
- Access and update data easily
- Perform operations like searching, sorting, and filtering
Why is it important to structure data?
Imagine trying to store 1,000 names, numbers, or results — data structures make this easy.
They are the building blocks of coding, especially for:
- Solving problems
- Writing clean, efficient code
What are the built in data types in Python?
Python has four main built-in data structures.
1. List: A list is a built-in data structure in Python that lets you store multiple items in a single variable. Lists are ordered, changeable, and allow duplicate values.
Example: #code
names = [“harish”, “keerthi”, “saanvi”]
print(names[0]) # output: harish
2. Tuple: A tuple is like a list, but there’s one big difference — tuples cannot be changed after they’re created. That means you can’t add, remove, or modify the items inside a tuple.
Example: #code
names = [“harish”, “keerthi”, “saanvi”]
print(names[1]) # output: keerthi
3. Dictionary: A dictionary in Python lets you store data using key-value pairs. Instead of using positions like in a list, you use a key to get the value. For example, {“name”: “Keerthi”, “age”: 24} stores a person’s info.
Example: #code
person = {“name”: “keerthi”, “age”: 24}
print(person[“name”]) # output: keerthi
4. Set: A set is a collection of unordered, unchangeable, and unique items in Python.
Example: #code
unique_names = {keerthi, harish, saanvi, keerthi}
print(unique_names) #output: harish, saanvi
Other Useful Data Structures
Stack: A stack in Python is a linear data structure that follows the Last-In-First-Out (LIFO) principle.
Queue: A queue is a linear data structure that follows the First-In-First-Out (FIFO) principle.
Linked List: Linked List is an abstract data type in Python that allows users to organize information in nodes, which then link to another node in the list.
Trees: Trees are non-linear data structures that store data hierarchically and are made up of nodes connected by edges.
Graphs: Graph data structures are data structures that consist of a collection of nodes or vertices connected by edges.
Final Thoughts:
Data Structures are the building blocks of Python programming. Mastering them makes your code cleaner, faster, and interview-ready.
